4-Hydroxybenzoic acid
| 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid | |
|---|---|
|
4-Hydroxybenzoic acid |
|
|
Other names
p-Hydroxybenzoic acid |
|
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 99-96-7 |
| PubChem | 135 |
| ChemSpider | 132 |
| DrugBank | DB04242 |
| KEGG | C00156 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:30763 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL441343 |
| Jmol-3D images | Image 1 Image 2 |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | C7H6O3 |
| Molar mass | 138.12 g/mol |
| Density | 1.46 g/cm³ |
| Melting point |
214–217 °C |
| (verify) (what is: /?) Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa) |
|
| Infobox references | |
4-Hydroxybenzoic acid is a monohydroxybenzoic acid, a phenolic derivative of benzoic acid. It is a white crystalline solid that is slightly soluble in water and chloroform but more soluble in polar organic solvents such as alcohols and acetone. 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid is primarily known as the basis for the preparation of its esters, known as parabens, which are used as preservatives in cosmetics. It is isomeric with 2-hydroxybenzoic acid, known as salicylic acid, a precursor to aspirin.
Contents |
Natural occurrence
4-Hydroxybenzoic acid can be found naturally in Cocos nucifera.[1] It is one of the main catechins metabolites found in humans after consumption of green tea infusions.[2]
Açaí oil, obtained from the fruit of the açaí Palm (Euterpe oleracea), is rich in p-hydroxybenzoic acid (892 ± 52 mg/kg), protocatechuic acid (630 ± 36 mg/kg) and ferulic acid (101 ± 5.9 mg/kg).[3]
Cryptanaerobacter phenolicus is a bacterium species that produces benzoate from phenol via 4-hydroxybenzoate.[4]
Chemical production
4-Hydroxybenzoic acid is produced commercially from potassium phenoxide and carbon dioxide in the Kolbe-Schmitt reaction.[5]
4-Hydroxybenzoic acid can also be produced in the laboratory by heating potassium salicylate with potassium carbonate to 240 °C, followed by treating with acid.[6]
Chemical reactions
It is about 10x less acidic than benzoic acid, Ka = 3.3 x 10−5 M at 19 °C:
- HOC6H4CO2H
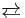 HOC6H4CO2− + H+
HOC6H4CO2− + H+
Safety
4-Hydroxybenzoic acid is popular antioxidant in part because of its low toxicity. The LD50 is 2200 mg/kg in mice (oral).
References
- ^ Profiling C6–C3 and C6–C1 phenolic metabolites in Cocos nucifera. Gargi Dey, Moumita Chakraborty and Adinpunya Mitra, Journal of Plant Physiology, Volume 162, Issue 4, 22 April 2005, Pages 375-381 doi:10.1016/j.jplph.2004.08.006
- ^ Catechin metabolites after intake of green tea infusions. P. G. Pietta, P. Simonetti, C. Gardana, A. Brusamolino, P. Morazzoni and E. Bombardelli, BioFactors, 1998, Volume 8, Issue 1-2, pp. 111–118, doi:10.1002/biof.5520080119
- ^ Pacheco-Palencia LA, Mertens-Talcott S, Talcott ST (Jun 2008). "Chemical composition, antioxidant properties, and thermal stability of a phytochemical enriched oil from Acai (Euterpe oleracea Mart.)". J Agric Food Chem 56 (12): 4631–6. doi:10.1021/jf800161u. PMID 18522407.
- ^ Cryptanaerobacter phenolicus gen. nov., sp. nov., an anaerobe that transforms phenol into benzoate via 4-hydroxybenzoate. Pierre Juteau, Valérie Côté, Marie-France Duckett, Réjean Beaudet, François Lépine, Richard Villemur and Jean-Guy Bisaillon, IJSEM, January 2005, vol. 55, no. 1, pages 245-250, doi:10.1099/ijs.0.02914-0
- ^ Edwin Ritzer and Rudolf Sundermann “Hydroxycarboxylic Acids, Aromatic” in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2002, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. doi: 10.1002/14356007.a13_519
- ^ C. A. Buehler and W. E. Cate (1943), "p-Hydroxybenzoic acid", Org. Synth., http://www.orgsyn.org/orgsyn/orgsyn/prepContent.asp?prep=CV2P0341; Coll. Vol. 2: 341
|
|||||||||||